If your toes are always cold, one reason could be poor blood flow -- a circulatory problem sometimes linked to smoking, high blood pressure, or heart disease. The nerve damage of uncontrolled diabetes can also make your feet feel cold to you. Other possible causes include hypothyroidism and anemia. A doctor can look for any underlying problems -- or let you know that you simply have cold feet.

Foot Pain
When your feet ache after a long day, you might just curse your shoes. After all, eight out of 10 women say their shoes hurt. But pain that’s not due to sky-high heels may come from a stress fracture, a small crack in a bone. One possible cause: Exercise that was too intense, particularly high-impact sports like basketball and distance running. The weakened bones of osteoporosis increase your risk.
When your feet ache after a long day, you might just curse your shoes. After all, eight out of 10 women say their shoes hurt. But pain that’s not due to sky-high heels may come from a stress fracture, a small crack in a bone. One possible cause: Exercise that was too intense, particularly high-impact sports like basketball and distance running. The weakened bones of osteoporosis increase your risk.
Dragging Your Feet
Sometimes the first sign of a problem is a change in the way you walk -- a wider gait or slight foot dragging. The cause may be the slow loss of normal sensation in your feet, brought on by peripheral nerve damage. About 30% of these cases are linked to diabetes. Nerve damage also can be due to infection, vitamin deficiency, and alcoholism. In many cases, no one knows what caused the nerve damage.
Sometimes the first sign of a problem is a change in the way you walk -- a wider gait or slight foot dragging. The cause may be the slow loss of normal sensation in your feet, brought on by peripheral nerve damage. About 30% of these cases are linked to diabetes. Nerve damage also can be due to infection, vitamin deficiency, and alcoholism. In many cases, no one knows what caused the nerve damage.
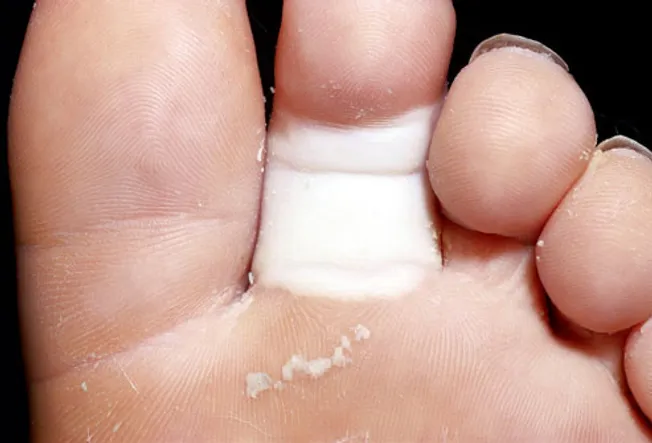
Red, White, and Blue Toes
Raynaud’s disease can cause your toes to turn white, then bluish, and then redden again and return to their natural tone. The cause is a sudden narrowing of the arteries, called vasospasms. Stress or changes in temperature can trigger vasospasms, which usually don’t lead to other health concerns. Raynaud’s may also be related to rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s disease, or thyroid problems.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
Heel Pain
The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis, inflammation where this long ligament attaches to the heel bone. The pain may be sharpest when you first wake up and put pressure on the foot. Arthritis, excessive exercise, and poorly fitting shoes also can cause heel pain, as can tendonitis. Less common causes include a bone spur on the bottom of the heel, a bone infection, tumor, or fracture
Clubbed Toes
In clubbing, the shape of the toes (and often the fingers) changes. The nails are more rounded on top and curve downward. Lung disease is the most common underlying cause, but it also can be caused by heart disease, liver and digestive disorders, or certain infections. Sometimes, clubbing runs in families without any underlying disease.
Raynaud’s disease can cause your toes to turn white, then bluish, and then redden again and return to their natural tone. The cause is a sudden narrowing of the arteries, called vasospasms. Stress or changes in temperature can trigger vasospasms, which usually don’t lead to other health concerns. Raynaud’s may also be related to rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s disease, or thyroid problems.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
Heel Pain
The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis, inflammation where this long ligament attaches to the heel bone. The pain may be sharpest when you first wake up and put pressure on the foot. Arthritis, excessive exercise, and poorly fitting shoes also can cause heel pain, as can tendonitis. Less common causes include a bone spur on the bottom of the heel, a bone infection, tumor, or fracture
Clubbed Toes
In clubbing, the shape of the toes (and often the fingers) changes. The nails are more rounded on top and curve downward. Lung disease is the most common underlying cause, but it also can be caused by heart disease, liver and digestive disorders, or certain infections. Sometimes, clubbing runs in families without any underlying disease.

Swollen Feet
This is usually a temporary nuisance caused by standing too long or a long flight -- especially if you are pregnant. In contrast, feet that stay swollen can be a sign of a serious medical condition. The cause may be poor circulation, a problem with the lymphatic system, or a blood clot. A kidney disorder or underactive thyroid can also cause swelling. If you have persistent swelling of your feet, see a physician.
Burning Feet
A burning sensation in the feet is common among diabetics with peripheral nerve damage. It can also be caused by a vitamin B deficiency, athlete’s foot, chronic kidney disease, poor circulation in the legs and feet (peripheral arterial disease), or hypothyroidism.
Sores That Don't Heal
Foot sores that will not heal are a major warning sign for diabetes. Diabetes can impair sensation in the feet, circulation, and normal wound healing, so even a blister can become a troublesome wound. Those sores also are prone to infection. Diabetics should wash and dry their feet and check them for any wounds every day. Slow-healing of sores also can be caused by poor circulation from conditions such as peripheral artery disease.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
Pain in the Big Toe
Gout is a notorious cause of sudden pain in the big toe joint, along with redness and swelling (seen here). Osteoarthritis is another culprit that causes pain and swelling. If the joint is rigid, it may be hallux rigidus, a complication of arthritis where a bone spur develops. Finally, turf toe is an ailment of athletes, particularly those who play on hard surfaces. It's caused by an injury to ligaments surrounding the joint.
Pain in the Smaller Toes
If you feel like you're walking on a marble, or if pain burns in the ball of your foot and radiates to the toes, you may have Morton’s neuroma, a thickening of tissue around a nerve, usually between the third and fourth toes. It is eight to 10 times more common in women than in men. It is caused by injury or too much pressure on the toes.
Itchy Feet
Itchy, scaly skin may be athlete’s foot, a fungal infection that's common in men between the ages of 20 and 40. A reaction to chemicals or skin care products -- called contact dermatitis -- can cause itching, too, along with redness and dry patches. If the skin on your itchy feet is thick and pimple-like, it may be psoriasis, an over-reaction of the immune system. Medicated creams can relieve the symptoms.
Claw Toe
This foot deformity can be caused by shoes that are tight and pinch your toes or by a disease that damages nerves, such as diabetes, alcoholism, or other neurological disorder. Your toes will be bent upward as they extend from the ball of the foot, then downward from the middle joint, resembling a claw. They may respond to stretching and exercises of the toes or you may need special shoes or even surgery.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
Foot Spasms
A sudden, sharp pain in the foot is the hallmark of a muscle spasm or cramp, which can last many minutes. Overwork and muscle fatigue are common causes. Other causes include poor circulation, dehydration, or imbalances in potassium, magnesium, calcium, or vitamin D levels in the body. The changing hormone levels of pregnancy or thyroid disorders may play a role. If spasms are frequent or severe, see a doctor. Strengthening exercises can help with muscle fatigue.
Dark Spot on the Foot
We associate skin cancer with the sun, so we’re not as likely to check our feet for unusual spots. However, a melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer, can develop even in areas that are not regularly exposed to the sun. Melanoma can even appear beneath the nail, where it might look like a black spot.
Yellow Toenails
Your toenails tell a lot about your overall health. A fungal infection often causes thickened yellow toenails. Thick, yellow nails also can be a sign of an underlying disease, including lymphedema (swelling related to the lymphatic system), lung problems, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Spoon-shaped Toenails
Sometimes an injury to the nail or frequent exposure to petroleum-based solvents can create a concave, spoon-like shape. However, iron deficiency also can cause this unusual shape.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
White Nails
Injury to the nail or illness anywhere in the body can cause white areas in the nails. If part or all of a nail separates from the nail bed (shown here), it can appear white -- and may be due to an injury, nail infection, or psoriasis. If the nail is intact and most of it is white, it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition including liver disease, congestive heart failure, or diabetes. Talk with your health care team about any concerns.
Pitting of the Nails
Pitting, or punctured-looking depressions in the surface of the nail, is caused by a disruption in the growth of the nail at the nail plate. It affects as many as half of people with psoriasis.
This is usually a temporary nuisance caused by standing too long or a long flight -- especially if you are pregnant. In contrast, feet that stay swollen can be a sign of a serious medical condition. The cause may be poor circulation, a problem with the lymphatic system, or a blood clot. A kidney disorder or underactive thyroid can also cause swelling. If you have persistent swelling of your feet, see a physician.
Burning Feet
A burning sensation in the feet is common among diabetics with peripheral nerve damage. It can also be caused by a vitamin B deficiency, athlete’s foot, chronic kidney disease, poor circulation in the legs and feet (peripheral arterial disease), or hypothyroidism.
Sores That Don't Heal
Foot sores that will not heal are a major warning sign for diabetes. Diabetes can impair sensation in the feet, circulation, and normal wound healing, so even a blister can become a troublesome wound. Those sores also are prone to infection. Diabetics should wash and dry their feet and check them for any wounds every day. Slow-healing of sores also can be caused by poor circulation from conditions such as peripheral artery disease.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
Pain in the Big Toe
Gout is a notorious cause of sudden pain in the big toe joint, along with redness and swelling (seen here). Osteoarthritis is another culprit that causes pain and swelling. If the joint is rigid, it may be hallux rigidus, a complication of arthritis where a bone spur develops. Finally, turf toe is an ailment of athletes, particularly those who play on hard surfaces. It's caused by an injury to ligaments surrounding the joint.
Pain in the Smaller Toes
If you feel like you're walking on a marble, or if pain burns in the ball of your foot and radiates to the toes, you may have Morton’s neuroma, a thickening of tissue around a nerve, usually between the third and fourth toes. It is eight to 10 times more common in women than in men. It is caused by injury or too much pressure on the toes.
Itchy Feet
Itchy, scaly skin may be athlete’s foot, a fungal infection that's common in men between the ages of 20 and 40. A reaction to chemicals or skin care products -- called contact dermatitis -- can cause itching, too, along with redness and dry patches. If the skin on your itchy feet is thick and pimple-like, it may be psoriasis, an over-reaction of the immune system. Medicated creams can relieve the symptoms.
Claw Toe
This foot deformity can be caused by shoes that are tight and pinch your toes or by a disease that damages nerves, such as diabetes, alcoholism, or other neurological disorder. Your toes will be bent upward as they extend from the ball of the foot, then downward from the middle joint, resembling a claw. They may respond to stretching and exercises of the toes or you may need special shoes or even surgery.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
Foot Spasms
A sudden, sharp pain in the foot is the hallmark of a muscle spasm or cramp, which can last many minutes. Overwork and muscle fatigue are common causes. Other causes include poor circulation, dehydration, or imbalances in potassium, magnesium, calcium, or vitamin D levels in the body. The changing hormone levels of pregnancy or thyroid disorders may play a role. If spasms are frequent or severe, see a doctor. Strengthening exercises can help with muscle fatigue.
Dark Spot on the Foot
We associate skin cancer with the sun, so we’re not as likely to check our feet for unusual spots. However, a melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer, can develop even in areas that are not regularly exposed to the sun. Melanoma can even appear beneath the nail, where it might look like a black spot.
Yellow Toenails
Your toenails tell a lot about your overall health. A fungal infection often causes thickened yellow toenails. Thick, yellow nails also can be a sign of an underlying disease, including lymphedema (swelling related to the lymphatic system), lung problems, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Spoon-shaped Toenails
Sometimes an injury to the nail or frequent exposure to petroleum-based solvents can create a concave, spoon-like shape. However, iron deficiency also can cause this unusual shape.
Read Also: What Your Nails Say About Your Health
White Nails
Injury to the nail or illness anywhere in the body can cause white areas in the nails. If part or all of a nail separates from the nail bed (shown here), it can appear white -- and may be due to an injury, nail infection, or psoriasis. If the nail is intact and most of it is white, it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition including liver disease, congestive heart failure, or diabetes. Talk with your health care team about any concerns.
Pitting of the Nails
Pitting, or punctured-looking depressions in the surface of the nail, is caused by a disruption in the growth of the nail at the nail plate. It affects as many as half of people with psoriasis.

No comments:
Post a Comment