Chewing on Ice
It’s natural and sugar free, so you might think ice is harmless. But munching on hard, frozen cubes can chip or even crack your teeth. And if your mindless chomping irritates the soft tissue inside a tooth, regular toothaches may follow. Hot foods and cold foods may trigger quick, sharp jabs of pain or a lingering toothache. Next time you get the urge for ice, chew some sugarless gum instead.

Playing Sports With No Mouth Guard
Whether you play football, hockey, or any other contact sport, don't get in the game without a mouth guard. This is a piece of molded plastic that protects the upper row of teeth. Without it, your teeth could get chipped or even knocked out when the action gets rough. Self-fitting mouth guards may be purchased at a store, or you can have one custom made by your dentist.
Bedtime Bottles
It’s never too early to protect teeth. Giving a baby a bedtime bottle of juice, milk, or formula, can put new teeth on a path to decay. The baby may become used to falling asleep with the bottle in his or her mouth, bathing the teeth in sugars overnight. It's best to keep bottles out of the crib.
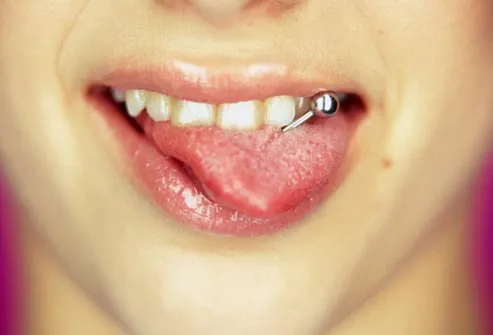
Tongue Piercings
Tongue piercings may be trendy, but biting down on the metal stud can crack a tooth. Lip piercings pose a similar risk. And when metal rubs against the gums, it can cause gum damage that may lead to tooth loss. The mouth is also a haven for bacteria, so piercings raise the risk of infections and sores. Bottom line, discuss the health risks with your dentist first.

Grinding Teeth
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, can wear teeth down over time. It is most often caused by stress and sleeping habits. This makes it hard to control. Avoiding hard foods during the day can reduce pain and damage from this habit. Wearing a mouth guard at night can prevent the damage caused by grinding while sleeping.
Cough Drops
Just because cough drops are sold in the medicine aisle doesn't mean they’re healthy. Most are loaded with sugar. So after soothing your throat with a lozenge, be sure to brush well. Whether the sugar comes from a cough drop or a hard candy, it reacts with the sticky plaque that coats your teeth. Then bacteria in the plaque convert the sugar into an acid that eats away at tooth enamel. Hello, cavities.

Gummy Candy
All sugary treats promote tooth decay, but some candies are harder to bear. Gummies stick in the teeth, keeping the sugar and resulting acids in contact with your enamel for hours. If your day just isn't the same without a gummy critter, pop a couple during a meal instead of as a separate snack. More saliva is produced during meals, which helps rinse away candy bits and acids.
Soda
Candy isn't the only culprit when it comes to added sugar. Sodas can have up to 11 teaspoons of sugar per serving. To add insult to injury, sodas also contain phosphoric and citric acids, which eat away at tooth enamel. Diet soft drinks let you skip the sugar, but they may have even more acid in the form of the artificial sweeteners.

Opening Stuff With Your Teeth
Opening bottle caps or plastic packaging with your teeth may be convenient, but this is one habit that makes dentists cringe. Using your teeth as tools can cause them to crack or chip. Instead, keep scissors and bottle openers handy. Bottom line, your teeth should only be used for eating.
Sports Drinks
There's no doubt a cold sports drink is refreshing after a good workout. But these drinks are usually high in sugar. Like soda or candy, sugary sports drinks create an acid attack on the enamel of your teeth. Drinking them frequently can lead to decay. A better way to stay hydrated at the gym is to chug sugar-free, calorie-free water.
Fruit Juice
Fruit juice is loaded with vitamins and antioxidants, but unfortunately most juices are also loaded with sugar. Some juices can have as much sugar per serving as soda. For example, there are only 10 more grams of sugar in orange soda than in orange juice. Fruits are naturally sweet, so look for juice that has no added sugar. You can also reduce the sugar content by diluting juice with some water.

Potato Chips
The bacteria in plaque will also break down starchy foods into acid. This acid can attack the teeth for the next 20 minutes -- even longer if the food is stuck between the teeth or you snack often. You might want to floss after eating potato chips or other starchy foods that tend to get stuck in the teeth.
Constant Snacking
Snacking produces less saliva than a meal, leaving food bits in your teeth for hours longer. Avoid snacking too frequently, and stick to snacks that are low in sugar and starch -- for example, carrot sticks.

Chewing on Pencils
Do you ever chew on your pencil when concentrating on work or studies? Like crunching on ice, this habit can cause teeth to chip or crack. Sugarless gum is a better option when you feel the need to chew. It will trigger the flow of saliva, which can make teeth stronger and protect against enamel-eating acids.
Drinking Coffee
Coffee's dark color and acidity can cause yellowing of the teeth over time. Fortunately, it's one of the easiest stains to treat with various whitening methods. Talk to your dentist if you're concerned about discoloration of your teeth.

Smoking
Cigarettes, as well as other tobacco products, can stain teeth and cause them to fall out as a result of gum disease. Tobacco can also cause cancer of the mouth, lips, and tongue. If you were looking for one more reason to quit, think of your smile.
Drinking Red Wine
The acids in wine eat away at tooth enamel, creating rough spots that make teeth more vulnerable to staining. Red wine also contains a deep pigment called chromogen and tannins, which help the color stick to the teeth. This combination makes it easy for the wine's red color to stay with you long after your glass is empty.
Drinking White Wine
You might think sticking to white wine would spare your teeth. But the acids still weaken the enamel, leaving the teeth porous and vulnerable to staining from other beverages, such as coffee. Swishing with water after drinking or using toothpaste with a mild whitening agent can fight the staining effects of red and white wines.

Binge Eating
Binge eating often involves excessive amounts of sweets, which can lead to tooth decay. Binging and purging (bulimia nervosa) can do even more damage to dental health. The strong acids found in vomit can erode teeth, making them brittle and weak. These acids also cause bad breath. Bulimia can lead to a variety of serious health problems, so be sure to talk to your doctor if you have been purging.
***



